Traditional Algorithms
- Work like a decision tree
- Based on a limited number of pre-defined rules
- Hard to detect P-waves due to low signal-to-noise ratio, possible overlapping with T-waves, variability with specific morphologies or diseases
- Lack specificity, creating a high rate of false alarms, which are a burden to manage
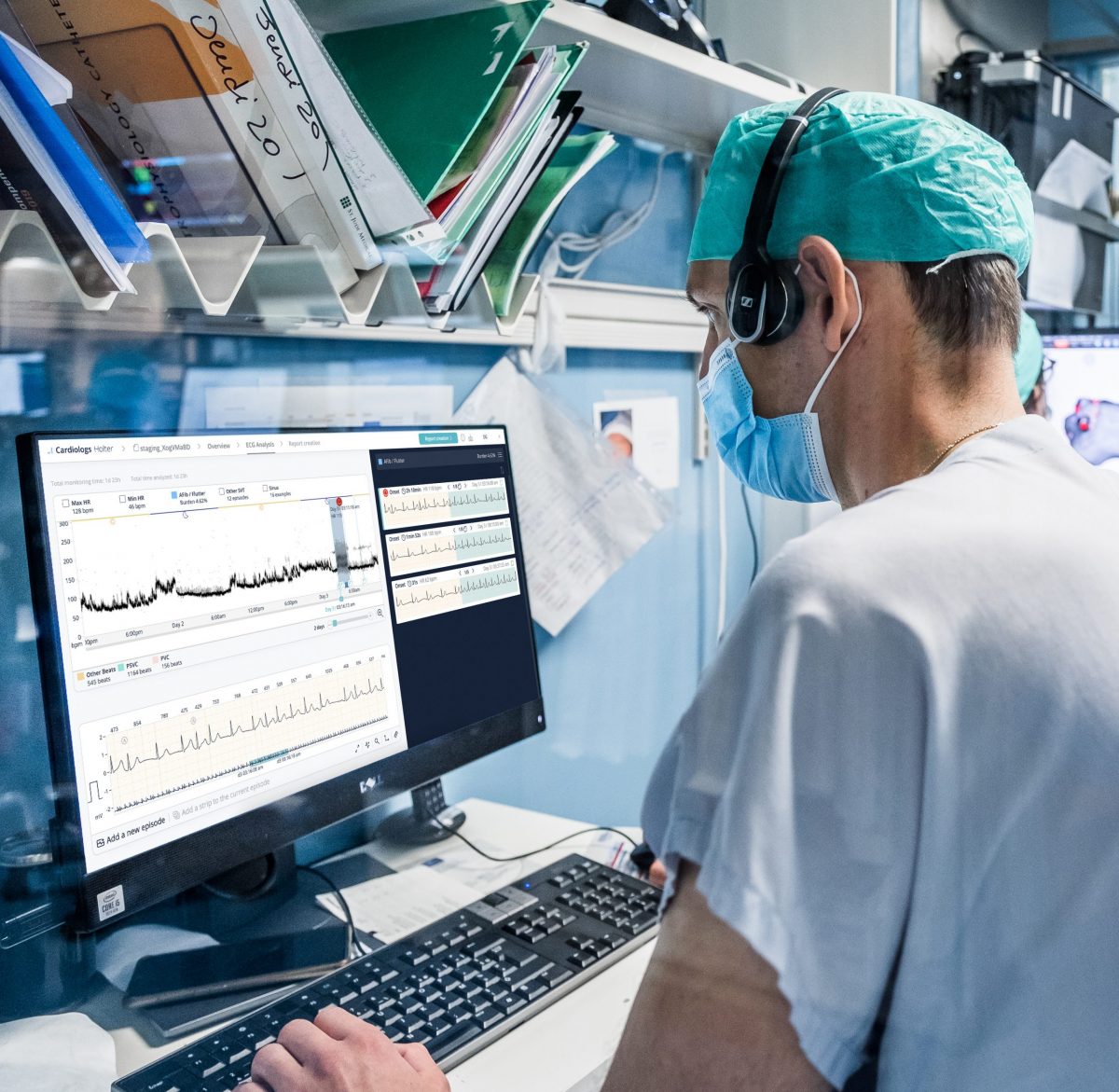
Cardiologs AI
- Based on deep learning technology that interprets the whole ECG¹
- Uses a similar thought process as the brain, handling multiple abnormalities and complex patterns at once
- Our delineation Deep Neural Network (DNN) segments different electrical waves (P, QRS, T). It was built upon 20M+ recordings²
- Improved specificity, dividing analysis times by two³
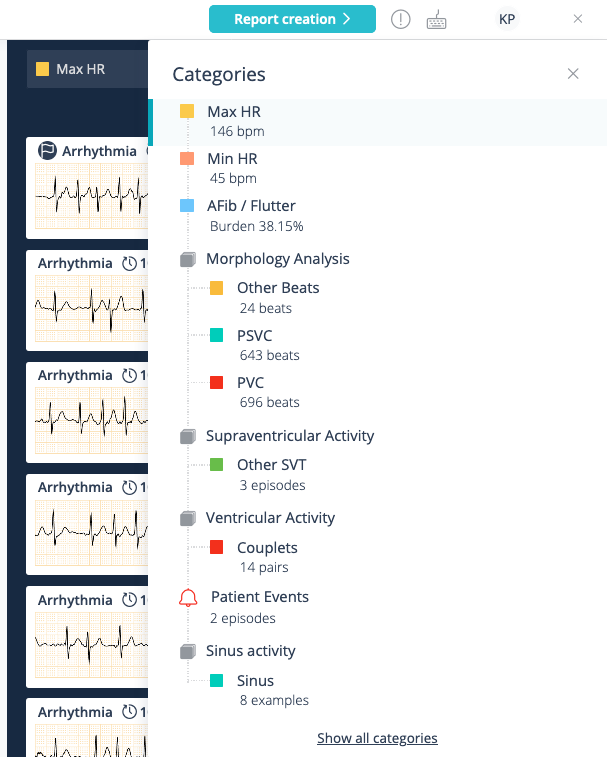
Our algorithm detects more than 20 types of events
- Pause
- Atrioventricular Block (second-degree, third-degree, advanced high-grade AV block)
- Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Premature Supraventricular Complexes (PSVCs), PSVC Couplets
- Premature Ventricular Complexes (PVCs)
- Ventricular Couplets, Ventricular Bigeminy, Ventricular Trigeminy
- Sinus rhythm, Bradycardia, Tachycardia
Validation of our AI algorithm
10 times reduction in AFib False Positives in Holter
Using the MIT-BIH public database, our Cardiologs AI algorithm was compared to the results of a reference RR interval-based method⁴. Our AI algorithm was shown to improve the specificity in Afib detection from 82.8% to 96.9% with comparable sensitivity.
Read the publication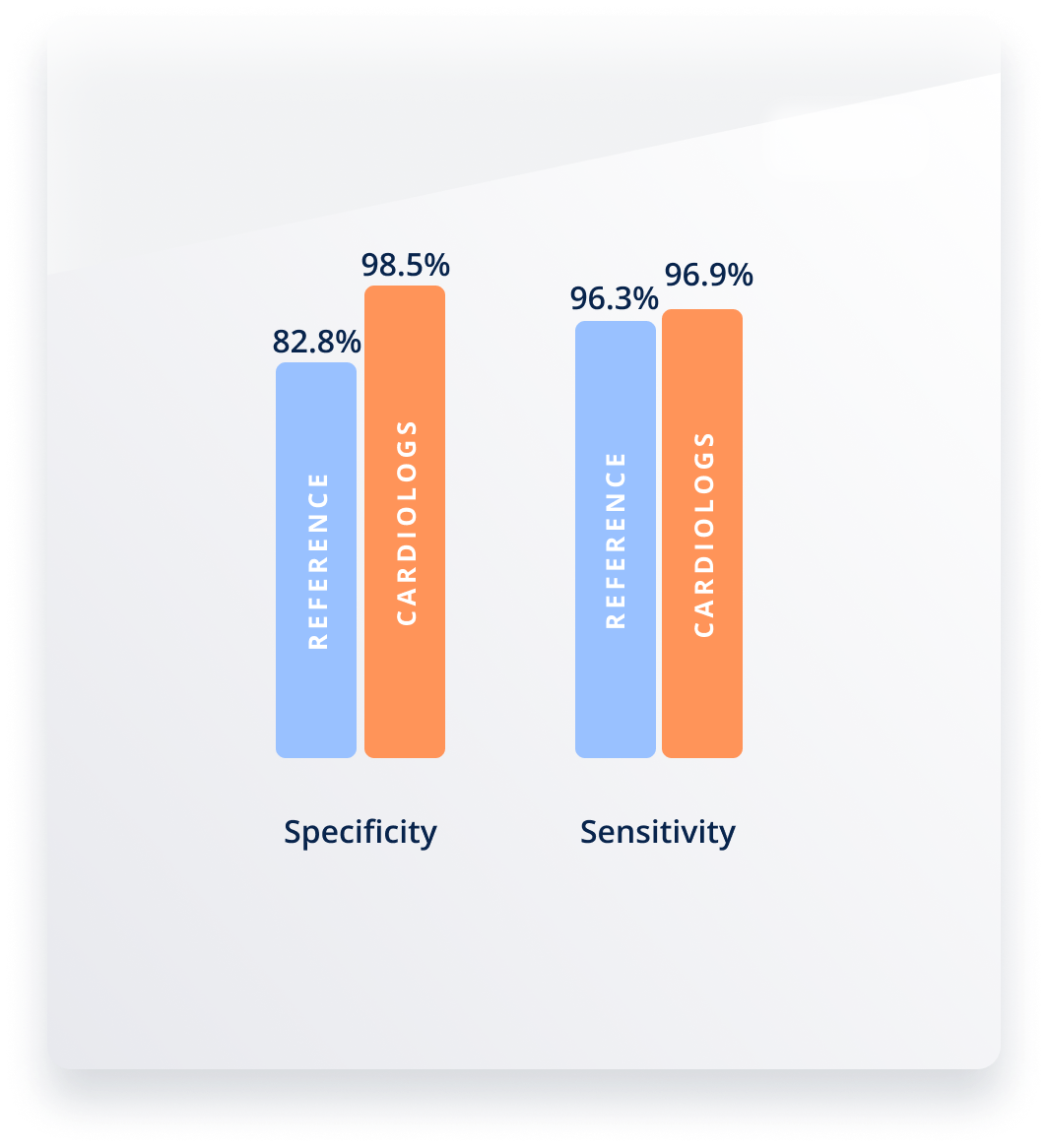
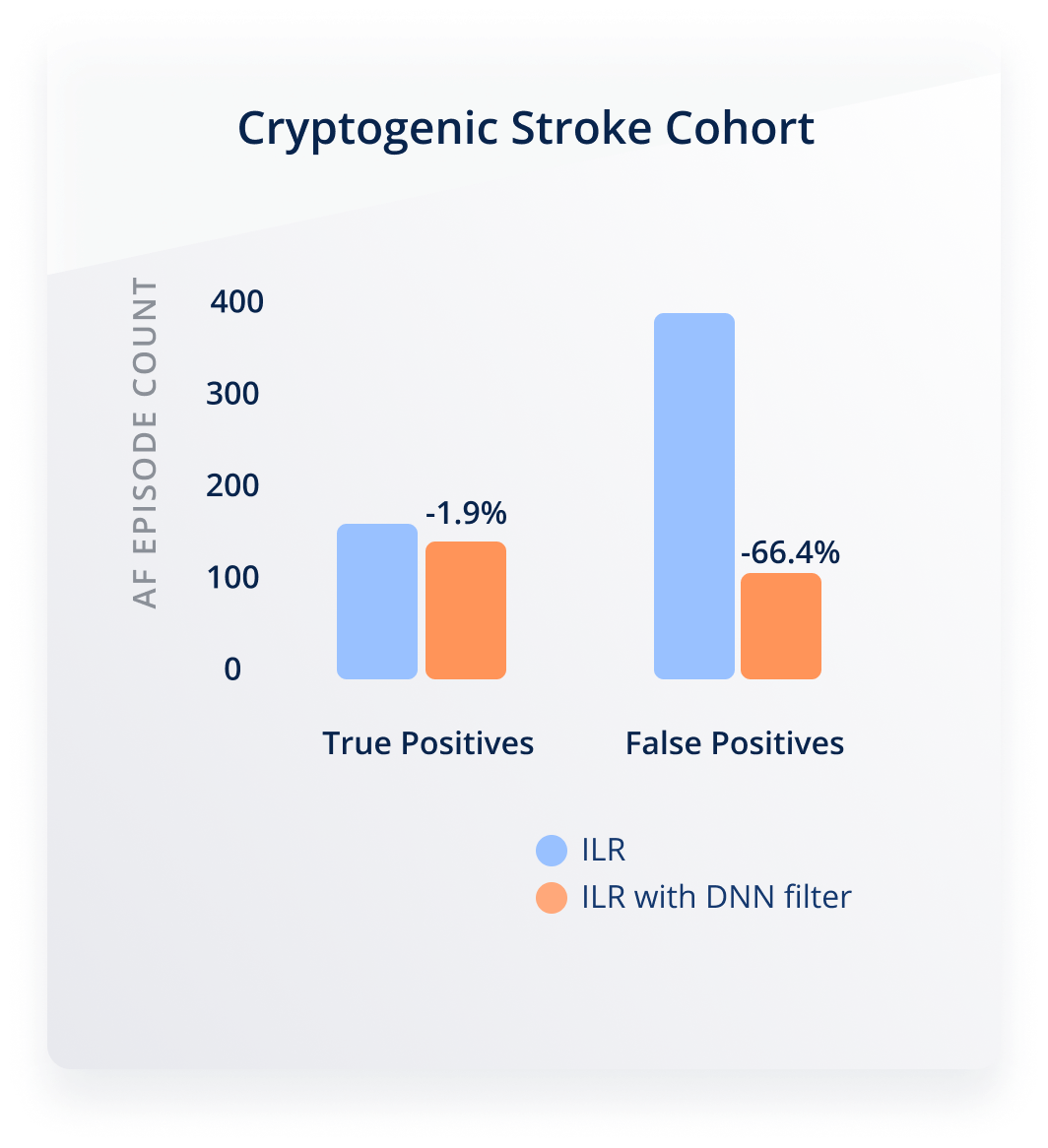
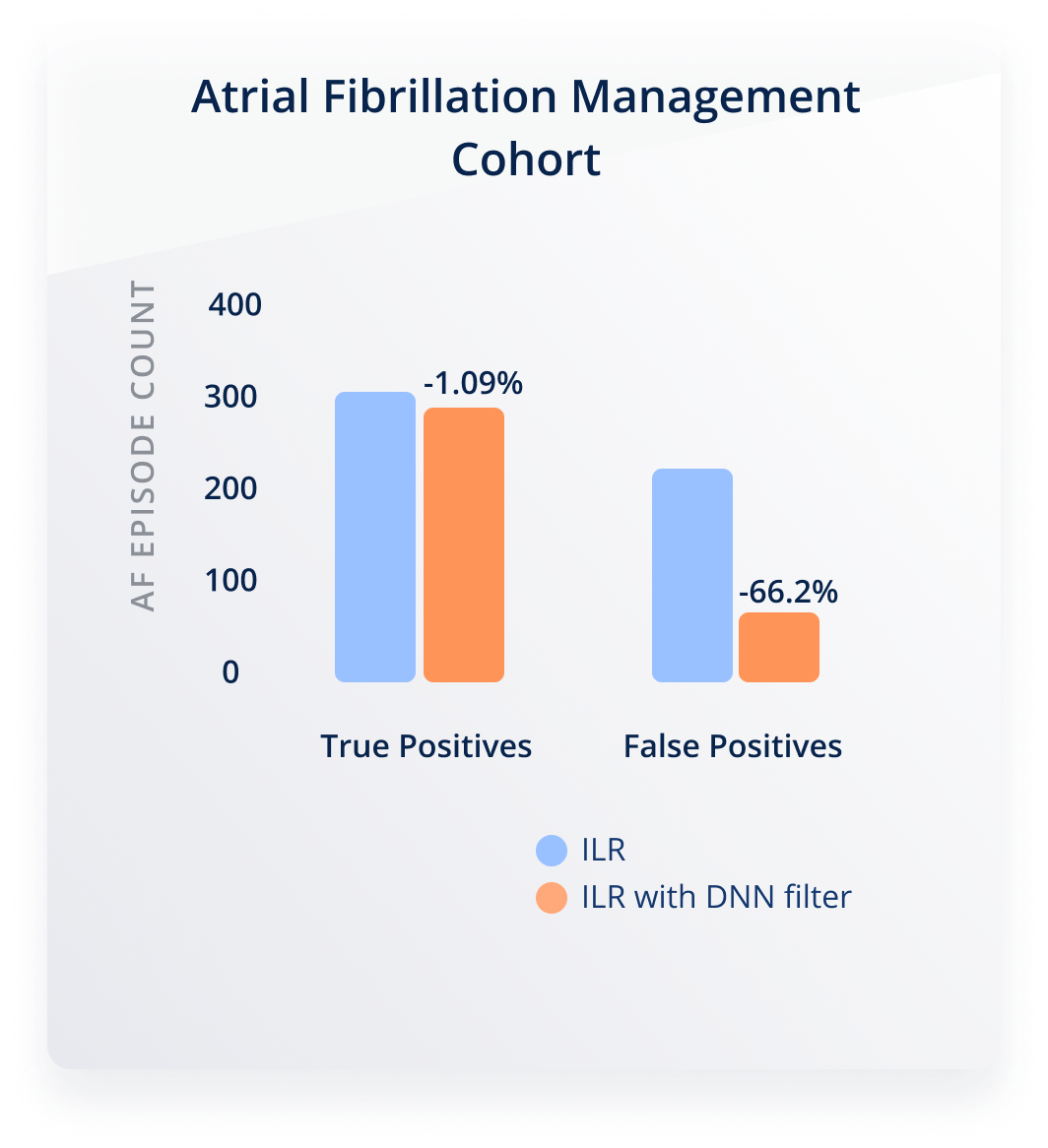
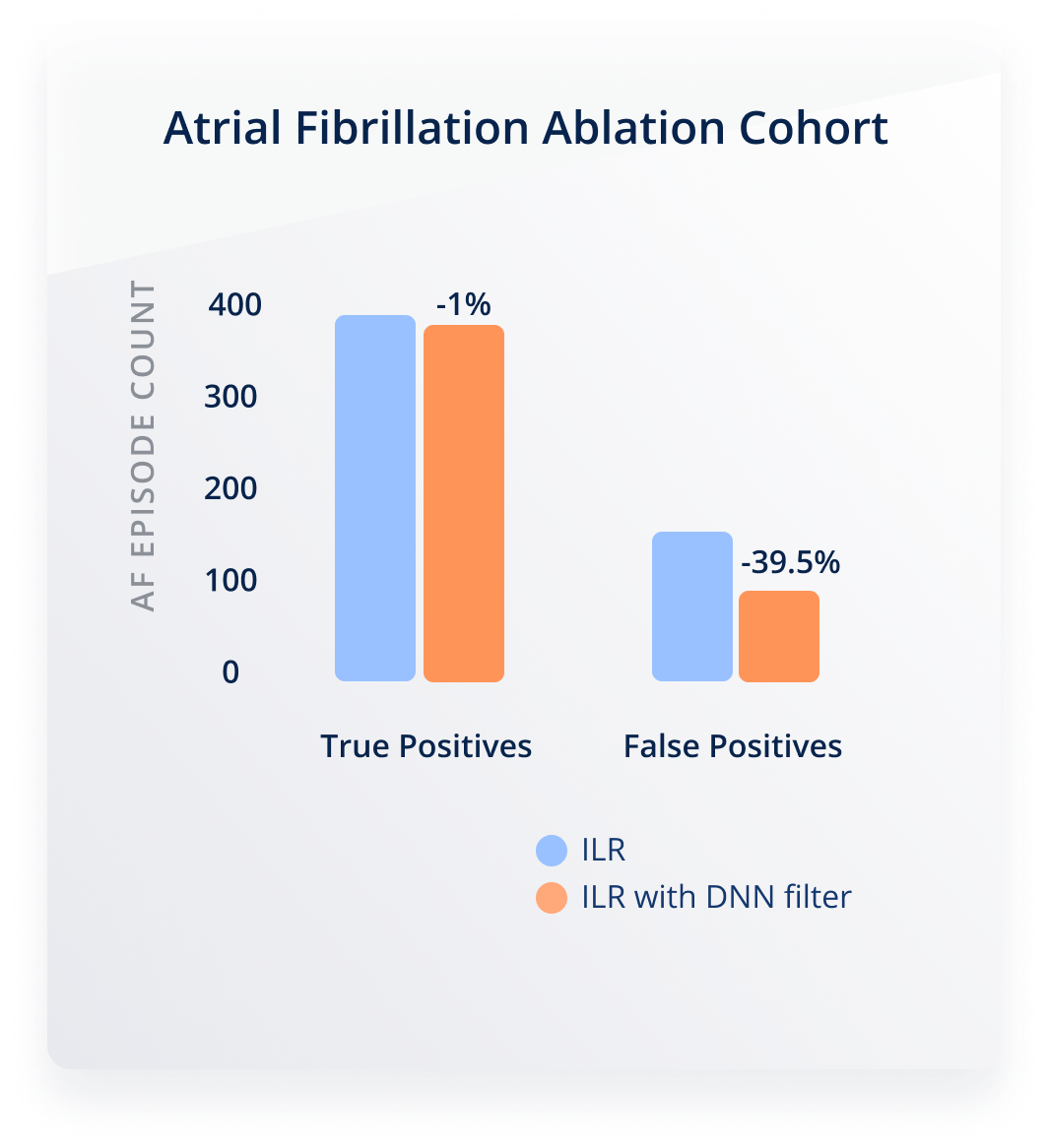
Reduction of False Positives by up to 70% in ICM
In a clinical study including 425 patients with ICMs, our algorithm was applied as a filter to all episodes detected by the ICM as Afib. It resulted in a reduction of false positive episodes by almost 70%, thereby considerably reducing the clinical burden of managing the data generated by those devices⁵.
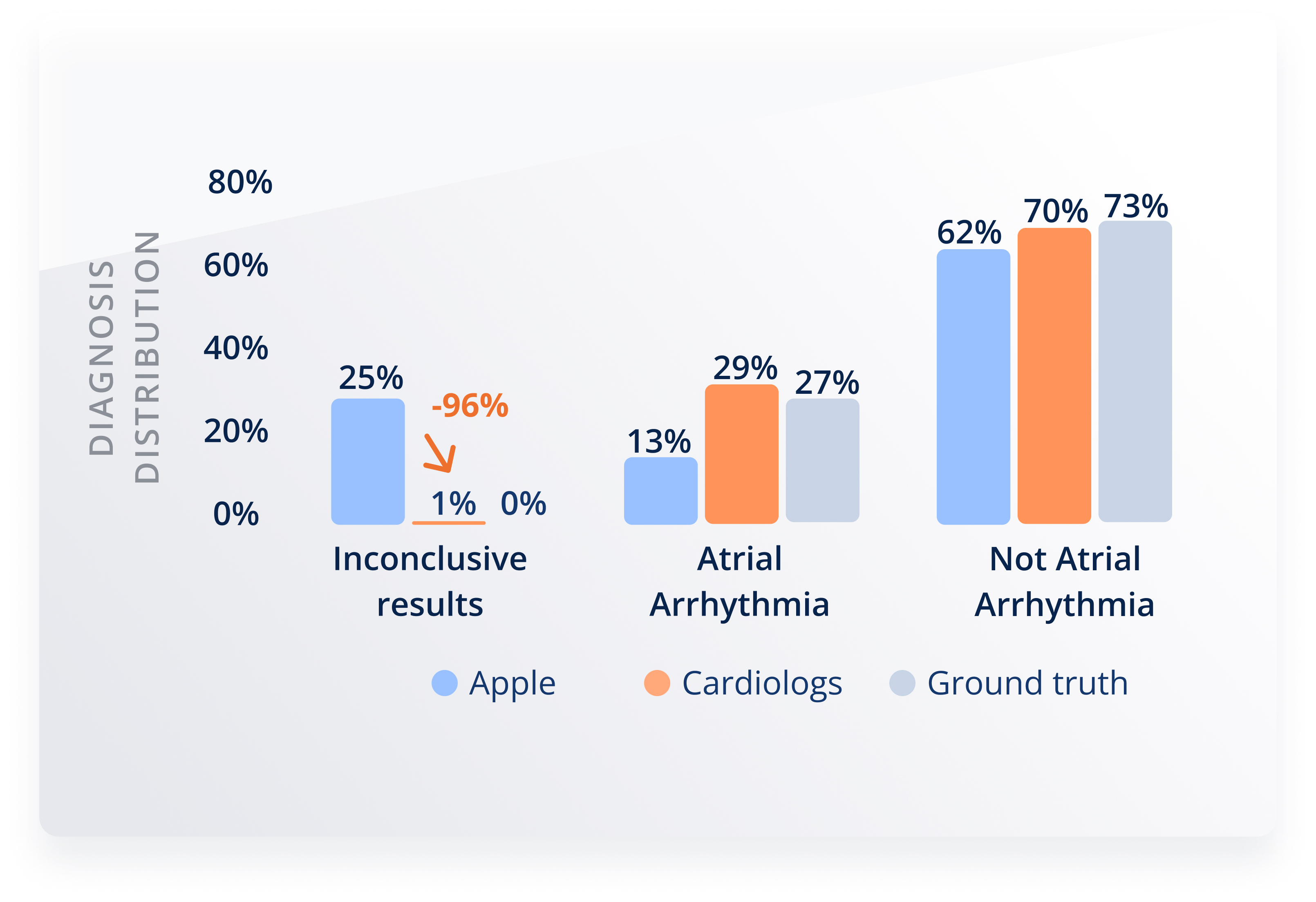
Read the publicationReduction of Inconclusive Results by 96% in Smartwatch ECGs
We compared the performance of our Cardiologs AI in smartwatch ECG to the results of the embedded algorithm. Results showed a reduction of inconclusive diagnoses from 25 out of 100 recordings to only 1 with Cardiologs AI. This decreases the time physicians need to spend reviewing data and reduces the risk of missed, delayed or incorrect diagnoses.
Read the abstract